Separation and purification of Nickel and Cobalt from pregnant leach solution by conventional vs ionic liquid as extractant: an overview
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.13133/2239-1002/18026Abstract
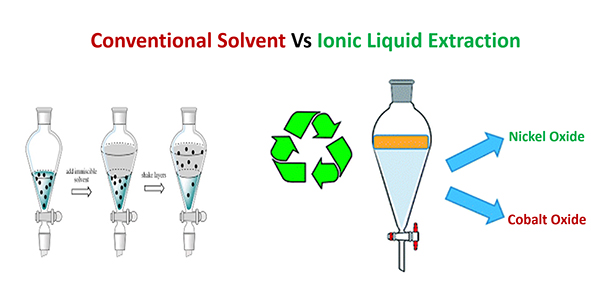
Solvent extraction (SX) is a common method used for nickel extraction, and conventional acidic extractants such as Cyanex 272, PC88A, and D2EHPA are typically employed. The extractant requires multi-step extraction and separating various metal impurities before the cobalt extraction stage. However, strict pH maintenance is needed during extraction, and strong acids must be used in stripping, which can negatively impact the environment and ecosystem. Treatments such as saponification are also required in conventional extractants to control the fall of pH and extraction value. The ionic liquid is a type of extract that is more environmentally friendly, harmless to the ecosystem and does not require further treatment such as saponification to get good results. One type that has been tried to separate cobalt from nickel is Phosphonium ionic liquids (PILs). The extraction value can exceed 95%, the use of acidic solutions is reduced, as well as proven to be more environmentally friendly. The advantages of ionic liquid are based on the lack of release of H+ ions in the by-product of the solvent extraction process and stripping agents can use deionized water very effectively. Further research on ionic liquid solvents such as PILs could bring us closer to the realization of an economically viable and environmentally friendly extraction process at an industrial scale.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Periodico di Mineralogia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

